Abstract
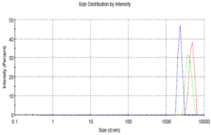
The present study was started with aim to design clotrimazole loaded polymeric microsphere based in situ ophthalmic gel for management of corneal fungal infections. The clotrimazole loaded microsphere was fabricated using various percentage of polylactide-co-glycolide polymer by solvent evaporation technique and evaluated for particle size, zeta potential and encapsulation efficiency. The polyvinyl alcohol was used as stabilizer. The formulation batch which showed good particle size and entrapment efficiency was selected for further study. The in situ ophthalmic gel of optimized drug loaded microsphere was formulated using various ratios of sodium alginate and hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose. The formulated gel was evaluated with respect to pH, in vitro gelling capacity, clarity, viscosity, in vitro antifungal activity and in vitro transcorneal permeation behavior. The fabricated drug loaded microspheres revealed acceptable particle size, zeta potential and encapsulation efficiency. The prepared in situ gels were clear and exhibited acceptable pH, rheological properties and in vitro gelation. The drug loaded microsphere based gel revealed superior in vitro antifungal activity against Aspergillus niger than conventional formulation and sufficient drug permeation across goat cornea. Thus, formulated clotrimazole loaded microsphere based in situ gel based systems can be a promising approach for sustained ophthalmic delivery of antifungal agents.
Full text article
References
Das, S., Suresh, P. K. 2011. Nanosuspension: a new vehicle for the improvement of the delivery of drugs to the ocular surface. Application to amphotericin B. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine, 7(2):242–247.
Garud, N., Garud, A. 2012. Preparation and In-vitro Evaluation of Metformin Microspheres Using Non-Aqueous Solvent Evaporation Technique. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 11(4):577– 583.
Kakkar, S., Karuppayil, S. M., Raut, J. S., Giansanti, F., Papucci, L., Schiavone, N., Kaur, I. P. 2015. Lipid polyethylene glycol based nano-ocular formulation of ketoconazole. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 495(1):276–289.
Kaur, I. P., Rana, C., Singh, H. 2008. Development of Effective Ocular Preparations of Antifungal Agents. Journal of Ocular Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 24(5):481–494.
Khames, A., Khaleel, M. A., El-Badawy, M. F., El-Nezhawy, A. O. H. 2019. Natamycin solid lipid nanoparticles sustained ocular delivery system of higher corneal penetration against deep fungal keratitis: preparation and optimization. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 14:2515–2531.
Klotz, S. A., Penn, C. C., Negvesky, G. J., Butrus, S. I. 2000. Fungal and Parasitic Infections of the Eye. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 13(4):662–685.
Makwana, S. B., Patel, V. A., Parmar, S. J. 2016. Development and characterization of in-situ gel for ophthalmic formulation containing ciprofloxacin hydrochloride. Results in Pharma Sciences, 6:1–6.
Mohanty, B., Majumdar, D. K., Mishra, S. K., Panda, K., Patnaik, S. 2015. Development and characterization of itraconazole-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for ocular delivery. Pharmaceutical Development and Technology, 20(4):458–464.
Müller, G. G., Kara-José, N., de Castro, R. S. 2013. Antifungals in eye infections: drugs and routes of administration. Brazilian Journal of Ophthalmology, 72(2):132–141.
Wu, Y., Liu, Y., Li, X., Kebebe, D., Zhang, B., Ren, J., Lu, J., Li, J., Du, S., Liu, Z. 2019. Research progress of in situ gelling ophthalmic drug delivery system. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 14(1):1– 15.
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.