Abstract
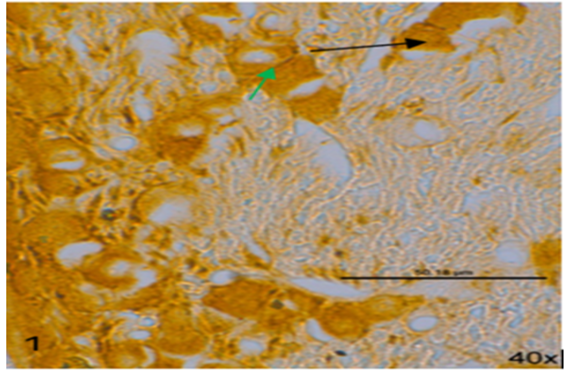
Migraine, a major public health problem, occurring due to the consequences of serial multi-pathophysiological changes in the trigeminal nerve ganglion leading to an imbalance in the excitation and inhibition. The glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, causing excitotoxicity to the sensory neurons leading to sensitization and nociception. The present study was done to determine the effects of Riluzole on the Nr2B subunits of NMDA receptors after inducing a migraine. The rats were treated with Riluzole after inducing migraine with nitroglycerin 10mg/kg. The nitroglycerin treated rats showed intense staining for NR2B subunits, and there was a decrease in the expression after Riluzole treatment. This study concludes that the NR2B subunits are upregulated during migraine and Riluzole can be used to control those upregulations by its neuroprotectant property.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.