Abstract
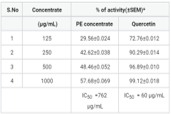
The genus Premna (Verbenaceae) comprises a group of more than 200 different trees, distributed in tropical and subtropical areas of the world. P. tomentosa (Verbanaceae) is a well-known medicinal plant used extensively for the treatment of various ailments. In the present study, the entire plant of different concentrates of aerial parts of Premna tomentosa was evaluated for its in-vitro anti-oxidant potential by superoxide scavenging activity, hydroxyl radical scavenging taking quercetin and ascorbate as the standard correspondingly. The results of antioxidant activity superoxide radical activity and hydroxyl potential were expressed in terms of % inhibition of generated free radicals respectively with respect to various concentrations. An IC50 value was recorded; methanolic concentrate of Premna tomentosa is more effective in superoxide radical activity, hydroxyl radical than that of EA and petroleum ether concentrate. The methanolic concentrate of Premna tomentosa and standard exhibited radical scavenging activity possessing IC50 values 225µg/mL and 60µg/mL (Superoxide Scavenging Activity), 288µg/mL and 65µg/mL (hydroxyl radical activity) correspondingly. All the above invitro studies clearly indicate that the methanolic concentrate of Premna tomentosa has better free radical scavenging activity. These invitro estimations point out that this methanolic concentrate of Premna tomentosa is a paramount source of expected antioxidant, which may be supportive in preventing the improvement of a variety of free radical induced diseases.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.