Abstract
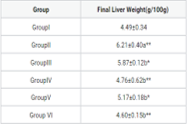
The current investigation was to examine the hepatoprotective potential of D.littoralis Nees. (family Acanthaceae) On paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. The aerial parts of D.littoralis Nees. The powder was concentrated with various solvents (PE, EA, and methanol) through Soxhlet concentrates and different crude concentrates utilized for hepatoprotective activity. Hepatotoxicity was induced by paracetamol (2g/kg b.wt.) on the 5th day of the investigational period and given orally. Paracetamol-induced rats to exhibit elevated activities of liver enzymes such as SGOT, SGPT, ALP, gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase (GGT), creatinine, urea, total bilirubin, total cholesterol & triglyc in serum. Furthermore, Oral administration of the ethyl acetate concentrates of D.littoralis (200 mg/ kgb.wt.) given rats were significant reduction the level of SGOT, SGPT, ALP, gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase (GGT) creatinine, urea, total bilirubin, total cholesterol & triglycerides when compared to other concentrates. They also significantly elevated the concentration of complete protein and albumin when compared to other concentrates. Thus, results suggested that ethyl acetate concentrates of D.littoralis could afford better hepatoprotective activity against paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity rats.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.