Abstract
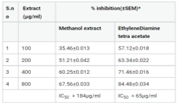
Cassia absus (Linn) (family Fabaceae) is generally known as “chaksu” in ayurvedic traditional system. The current study, aerial parts of different concentrates (concentrates (Pet.ether, ethyl acetate and methanol) of Cassia absus were evaluated for its in-vitro antioxidant potential by Superoxide radical, Iron chelating activity taking activity taking quercetin , Ethylenediamine tetraacetate as the standard respectively and total phenol content was estimated as equivalent to gallic acid. An IC50 value was originate that methanolic concentrates of Cassia absus more efficient in Superoxide radical, Iron chelating activity compared EA & PE concentrates. The methanolic concentrates of Cassia absus and standard exhibited antioxidant potential possessing IC50 217µg/ml & 60µg/ml (Superoxide radical). 184µg/ml & 65µg/ml (Iron chelating) respectively. The methanolic and EA concentrates of Cassia absus showed the total phenolic content (10.22 ± 0.40, 4.03 ± 0.47) respectively. The difference in scavenging potential of the extracts can be due to variation in the percentage of bioactive compound present in different solvents. Invitro antioxidant studies obviously show methanolic concentrates of Cassia absus have better antioxidant activity due to the presence of total phenolic content. This result indicate that aerial parts of methanolic concentrates Cassia absus could serve as natural antioxidant, which may be useful in prevent free radical induced diseases.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.