Abstract
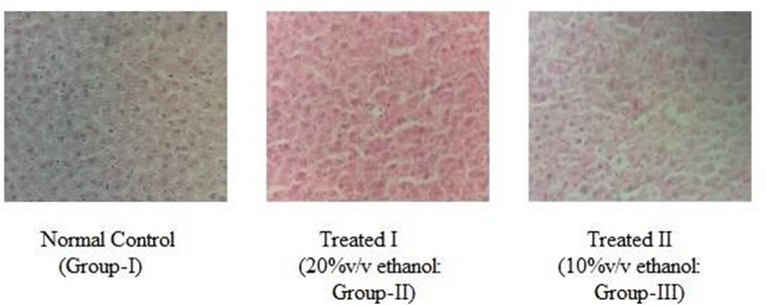
To investigate the effect of ethanol induced liver toxicity in male Wister albino rats. The liver toxicity was induced by the chronic administration of ethanol to the animals at the 20%v/v, 10%v/v respectively for 28 days at daily basis. The liver toxicity was assessed by the estimation of liver marker enzymes and liver histopathological studies. The chronic induction of ethanol in rats, liver marker enzymes like aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine ami- notransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP) , lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), total bilirubin (TB), direct bilirubin (DB) levels were significantly elevated (P<0.0001) when, compared to the normal animals. Ethanol is one of the most widely used and abused drugs and increasing lipid levels in humans and experimental animals. Liver damage seen in chronic ethanol consumption appears to be modulated by kupffer cell activation. Chronic ethanol treatment has been shown to enhance oxidative stress in liver tissues. Ethanol induced oxidative stress is a major role in the mechanism of hepatotoxicity. In the present study was revealed that the chronic consumption of ethanol treated rats shows significantly increased liver marker enzymes and severe damage to liver tissues.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.