Abstract
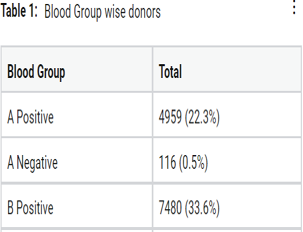
Microbiological safety is very important aspect of blood transfusion services (BTS). Viral infectious agents possess a great risk of transfusion transmitted disease. On the one hand, blood or component transfusion is a lifesaving modality but on the other hand it can cause great mortality or morbidity in recipient if not used judiciously. The main aim of the study is to evaluate the prevalence of HIV, HBV, HCV, Syphilis and Malaria amongst all types of donors donated at blood bank of Sir Sunderlal Hospital, Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi during the year 2017. This was a retrospective study. Total donation during that period was 22255 units. A detailed questionnaire was given to the donors for registration. A total of 226 units (1.01%) were seropositive. The sero-prevalence of HIV, HBV, HCV, and Syphilis were 0.9% (21), 0.79% (177), 0.09% (22), 0.02% (6) respectively. No cases of malaria were detected. TTI can be reduced by motivating maximum voluntary blood donation, reducing replacement donation, public information and donor education awareness programme, stringent donor screening criteria and vigilance of error.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.