Abstract
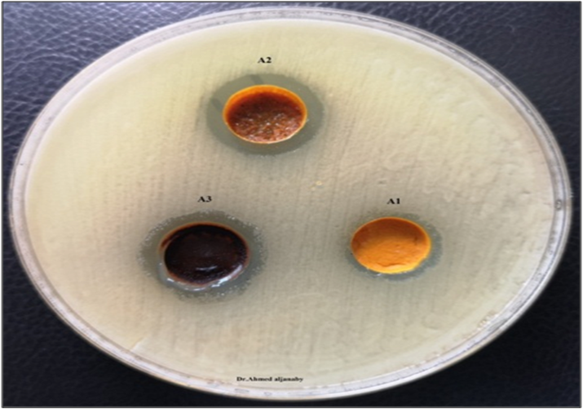
Schiff bases derivatives are one of the most important compounds that have been used in many biological applications such as antimicrobial activity. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus are two of the most important pathogenic bacteria that cause wound infection in Iraq and many developing countries. This research involves a synthesis of some Schiff bases compounds [A1 – A3] that were prepared from the condensation of [4- chlorobenzaldehyde, 4-bromobenzaldehyde, and 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde] in absolute ethanol. All of these compounds are characterized by [FTIR] spectroscopy. The antibacterial activity test was done according to agar well diffusion method for all derivative compounds with a concentration of 100 mg/ml and 200 mg/ml for each compound. The derivative compound A3 with a concentration of 200 mg/ml had an excellent antibacterial effect against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus with a diameter of inhibition zone of 18.417 ± 0.54645 and 16.000 ± 0.57735, respectively. Schiff bases derivatives synthesis compounds in this study (A1 and A2) can be considered as suitable antibacterial materials and can be used as raw materials to the synthesis of new ointment.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.