Abstract
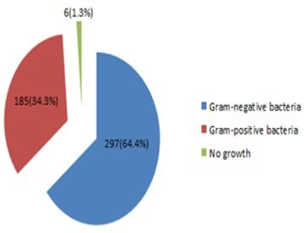
Citrobacter freundii is one of the most causative agents of urinary tract infection in human due to their high antimicrobials resistance. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the ability of Citrobacter freundii to resist to fifteen antimicrobials. A total of 461 urine samples were collected from patients infected with urinary tract infection, females and males, age groups between 18 to 60 years old performed in Al-Najaf central hospital in Al-Najaf City, Iraq, during April to December 2018. Antimicrobials susceptibility testing was performed by disc diffusion method according to the Kirby-Bauer method onto Mueller Hinton agar surface. There were 30 isolates (6.5%) diagnosed as Citrobacter freundii. Antimicrobial resistance rate of the 30 isolates to Amoxicillin and Chloramphenicol were all high (25 isolates 83.4%), Ciprofloxacin, Streptomycin and Sulfonamide (24 isolates 80%). The good resistance rate was observed for Penicillin, Amoxiclav and Ceftazidime (21 iso- lates 70%). The moderate resistance rate was observed for Cefotaxime (19 isolates 63.3%), Ceftriaxone (20 isolates 66.7%), Gentamicin (15 isolates 50%), Tobramycin (18 isolates 60%) and Erythromycin (20 isolates 66.7%). The lowest resistance rate was observed for Tetracycline (19 isolates 63.3%). While Imipenem provided full antibacterial activity (30 isolates 100%). Of the total 30 isolates, 22 (73.3%) were multi-drug resistance, 8(26.7%) exten- sive-drug resistance and no isolates were pan-drug resistance. While 19 isolates (63.3%) were extended-spectrum beta-lactamase producing Citrobacter freundii. Citrobacter freundii has highly resistant against most antimicrobials and became more dangerous bacteria cause urinary tract infection.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.