Effects of atmospheric endocrine disruptors from the city of Ouagadougou on female reproductive function in the Wistar rat
Abstract
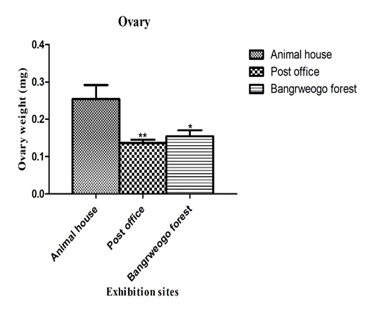
Anthropogenic activities contribute to the emission of various chemical particles and organic compounds into the atmosphere, either as volatile substances or through combustion, which pollute the air. Despite multiple pollution sources in Burkina Faso, limited research has been conducted on the effects of exposure to these pollutants, especially in Ouagadougou. While dietary exposure has been well-documented, the health risks associated with respiratory exposure remain poorly understood. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of atmospheric endocrine disruptors on female reproductive function in laboratory animals (Wistar rats). Thirty female Wistar rats were exposed at three locations in Ouagadougou for six months, with ten rats per site. The animals were weighed biweekly, and at the end of the study, they were euthanized. Organs, including ovaries, uterus, adrenal glands, and kidneys, were collected and weighed. Hormone levels were determined using the Cobas 6000® instrument, combining clinical chemistry and immunoanalysis. The results showed a significant reduction in weight gain in exposed rats compared to controls. Hormonal assays revealed decreased hormone levels, and biochemical and histological analyses confirmed the effects of exposure. Significant differences were observed in the number of affected animals between the Post Office site, Bangrweogo forest, and control sites. Atmospheric endocrine disruptors had adverse effects on the female reproductive function of rats, highlighting the health risks associated with pollution exposure.
Full text article
Generated from XML file
Authors
Bengyende, S. ., Sana, A. D. ., Kabore, T. J. L. ., Ouedraogo, E. ., Webike-mindamou, E. J. ., & Bayala, B. . (2025). Effects of atmospheric endocrine disruptors from the city of Ouagadougou on female reproductive function in the Wistar rat. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 16(3), 46–53. https://doi.org/10.26452/ijrps.v16i3.4790
Copyright (c) 2025 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.