Assessment of antioxidant activity and hypoglycemic and anti-hyperglycemic effects of the hydroethanolic extract of the trunk bark of Lannea acida A. Rich. (Anacardiaceae) in male NMRI mice
Abstract
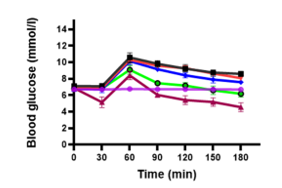
Lannea acida A. Rich (Anacardiaceae) is a plant widely used in African traditional medicine to treat various ailments, including diabetes and infertility. This study aimed to evaluate the antioxidant, hypoglycemic, and anti-hyperglycemic activities of the hydroethanolic extract from its trunk bark in male NMRI mice. Antioxidant activity was assessed using DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) and ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assays. Hypoglycemic effects were tested in fasting normoglycemic mice divided into five groups (n=5). The anti-hyperglycemic activity was evaluated via an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) on five groups of NMRI male mice (n=5). The extract showed an IC50 of 0.630 ± 0.003 mg/mL and a ferric ion reducing capacity of 393.13 ± 20.13 mg EAA/g. Oral administration of the extract at 40, 100, and 200 mg/kg body weight (bw) did not produce hypoglycemic effects compared to glibenclamide. However, at 200 mg/kg bw, the extract slightly reduced glucose-induced hyperglycemia (4 g/kg bw), though not significantly. This effect was weaker than that of glibenclamide (5 mg/kg). These findings suggest that Lannea acida possesses antioxidant and mild anti-hyperglycemic properties without inducing hypoglycemia, supporting its potential use in developing affordable phytomedicines.
Full text article
Generated from XML file
Authors
Koussoube, A. ., DA, F. L. ., Doukoure, M. ., Tindano, B. ., Kabore, T. J. L. ., Ouedraogo, E. ., & Bayala, B. . (2025). Assessment of antioxidant activity and hypoglycemic and anti-hyperglycemic effects of the hydroethanolic extract of the trunk bark of Lannea acida A. Rich. (Anacardiaceae) in male NMRI mice. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 16(2), 61–69. https://doi.org/10.26452/ijrps.v16i2.4755
Copyright (c) 2025 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.