Long-term exposure to sildenafil-adulterated herbal aphrodisiacs induces oxidative and functional alterations in the prostate and seminal vesicles of male rats
Abstract
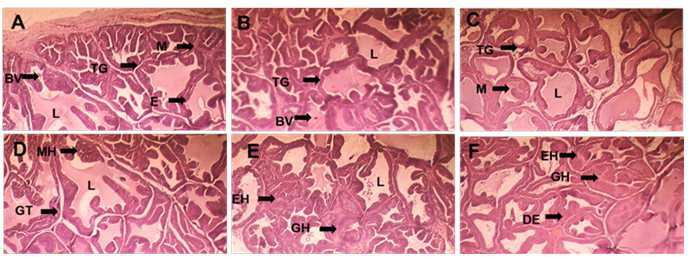
The unregulated use of herbal aphrodisiacs adulterated with synthetic drugs such as sildenafil represents a growing public health concern, particularly in developing regions. This study investigated the chronic toxicological effects of two such formulations (AT and CM) on the prostate and seminal vesicles of male Wistar rats. Animals were orally administered AT or CM extracts containing 1 mg/g of sildenafil at doses of 50, 100, or 200 mg/kg body weight for 90 days. Biochemical analyses revealed significant reductions in seminal vesicle fructose concentration and prostatic acid and alkaline phosphatase activities, indicating secretory dysfunction. Oxidative stress was confirmed by elevated malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and significant reductions in antioxidant enzymes, including SOD, CAT, GPx, and reduced glutathione. Histopathological examinations showed epithelial hyperplasia, glandular degeneration, and atrophy in both glands, particularly in high-dose groups. These findings highlight that chronic exposure to sildenafil-adulterated herbal products disrupts accessory gland function through oxidative stress and epithelial damage, raising concerns about their unregulated use and urging the implementation of tighter safety regulations and public awareness initiatives.
Full text article
Generated from XML file
Authors
Ouedraogo, N. E. J. A. ., Tindano, B. ., Doukouré, M. ., Yougbaré, W. J. R. ., Ouedraogo, E. ., Kaboré, J. L. ., Koussoubé, A. A. ., Sana, D. ., Bengyende, S. ., & Bayala, B. . (2025). Long-term exposure to sildenafil-adulterated herbal aphrodisiacs induces oxidative and functional alterations in the prostate and seminal vesicles of male rats. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 16(3), 14–23. https://doi.org/10.26452/ijrps.v16i3.4787
Copyright (c) 2025 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.