Abstract
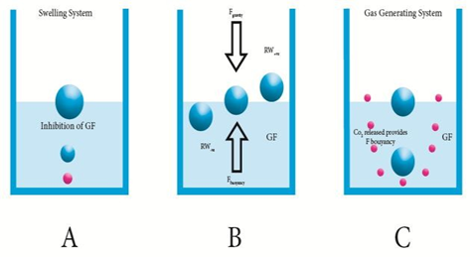
Currently, several approaches have been utilized in the extension of gastric residence time which includes FDDS, swelling and expanding systems, bio-adhesive systems, modified shape systems and high density systems. Among the gastro retentive dosage forms, floating dosage forms are coming out as a predicting dosage forms. Floating drug delivery systems (FDDS) have bulk density less than the gastric fluid contents and so, rest float on the stomach contents for a sustained period of time and ejecting the drug slowly at a desired rate from the system and enhance the bio-availability of the drug having narrow absorption window. Various components like hydrocolloids, inert fatty materials and buoyancy increasing agents can be used to formulate floating dosage forms. Various categories like antacids, anti-diabetic, anti- fungal and anticancer drugs are formulated into FDDS. The present review article addresses briefly about the back ground, advantages, disadvantages applications, approaches, and future aspects of floating drug delivery systems. This review also emphasizes about characterization parameters such as FT-IR, DSC, X-RD and evaluation parameters like floating time, drug release and swelling studies are also discussed.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.