Abstract
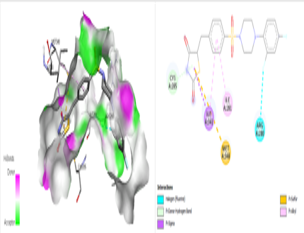
Diabetes Mellitus is the most common disease that poses a challenge to human health due to its secondary complications and resistance. Therefore, an attempt was made to synthesize novel compounds from thiazolidinedione moiety to treat the disease effectively and target diabetic complications. The synthesized compounds were tested for their physical parameters and characterised using NMR and IR spectra. They were also evaluated for STZ induced anti-diabetic activity in albino rats. The Compounds P5, II A8 and A9 were found effective in comparison with a standard drug, Pioglitazone. The other compounds were also effective but a reduction in activity is seen might be due to the inefficient binding to the PPAR receptors.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.