Abstract
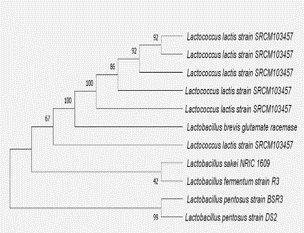
The research on the isolation of novel lactic acid bacteria (LAB) strains from different fermented plant beverages is receiving immense attention for their significant health benefits towards human health. The present study aimed to isolate and categorize various functional attributes of Lactobacillus pentosus DS2 isolated from fermented black carrot beverage. The isolated L. pentosus DS2 strain exhibited resistance to acid and higher salt concentrations. The isolated strain was identified by using 16S rRNA gene sequences. L. pentosus DS2 showed high survivability of about 6.75 to 7.02 log CFU/ml from pH (2-8) and at a different salt concentration (1-10%) log CFU/ml ranged from 7.92 to 6.41 log CFU/ml. According to the obtained results, auto-aggregation as well as cell surface hydrophobicity was about 16.2 ± 0.35 and 90 ± 0.21 % respectively, while co-aggregation value was 72.5 ± 2.12 and 82 ± 1.41% with Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus respectively. The enzymatic screening was performed and estimated as 0.54 ± 0.01, 103 ± 1.41, and 80.5 ± 2.89 U/mL of amylase, protease, and phytase. Cholesterol removal by L. pentosus DS2 was 47.15 ± 0.41%. The adherence levels by L. pentosus DS2 to different cell lines such as Caco-2 and HT-29 ranged from 17.65 ± 0.25 to 19.79 ± 0.31% respectively. Antibiotic susceptibility pattern obtained showed a different degree of antibiotics sensitivity, such as resistance to ampicillin. Thus, the isolated L. pentosus DS2 has all the desired properties to be used as a potential probiotics strain.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.