Abstract
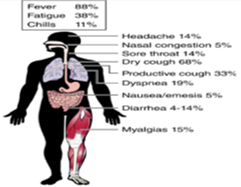
Coronaviruses was discovered in the mid-1960s that affect humans. In 2019, Wuhan city of Hubei, China, there was an out-break of "coronavirus disease (COVID-19)" which is the result of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) which is induced by a novel enveloped virus having single-stranded RNA. It transmitted rapidly affecting more than 200 countries globally, so, the World Health Organization has declared it as a pandemic. SARS-CoV-2 presently is a 7th amongst known coronaviruses that cause infection in people, after 229E and OC43 (earliest studied viruses in human patients suffering from a common cold). It has infected humans in all age groups, of all ethnicities, both males and females while spreading through communities at an alarming rate. Infected patients experience common cold-like symptoms along with raised temperature, non-productive coughing and difficulty to breathe. It is considered as a relative of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and the Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), COVID-19 is caused by a beta coronavirus named SARS-CoV-2, which affects the lower respiratory tract. Besides, SARS-CoV-2 also harms different organs. Till today, there is comprehensive knowledge about the extent and management of COVID-19-related disorders other than pulmonary system. The present review is an overview of systemic manifestations of COVID-19 that may affect gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, urinary, reproductive, hepatocellular or neurological systems.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.