Development and Evaluation of Topical Polyherbal Formulations for their Antimicrobial Potential
Abstract
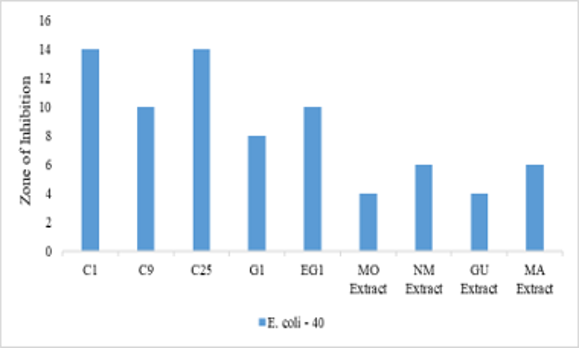
The different types of skin diseases caused due to microorganisms. In recent years the use of the traditional medicinal system was increased because of more minor side effects and cost effective. The single herbal drugs were found to be less potent, which can be improved by utilizing more than one herb in the single formulation, known as polyherbal formulation. The present work involved the development and evaluation of the different polyherbal formulations (cream, gel, and emulgel) using natural ingredients. The aim of the present work is to produce a formulation with improved antimicrobial potency and stability of formulations when compared with the individual extracts of herbal drugs. All the prepared formulations were tested against various microbial strains and concluded that the polyherbal formulations (C25, G1, EG1) were found potent against most selected strains. The prepared formulations can be used as a multipurpose formulation.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.