Abstract
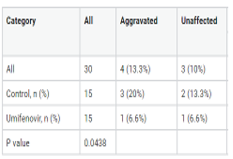
The coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak was initially reported in Wuhan, China in December 2019. Many cases of pneumonia without any apparent cause were described to be associated with seafood and wet markets in Wuhan. At present, there are no effective antiviral drugs to treat COVID-19. Umifenovir is a broad-spectrum antiviral drug used for treating several viral infections, and it reportedly inhibits SARS-CoV replication in vitro. This exploratory randomized and controlled study recruited 30 COVID-19 patients admitted to the hospital until May 18, 2020. Fifteen (15) eligible patients randomly allocated underwent umifenovir therapy (600 mg/d). Time to clinical recovery (TTCR), clinical characteristics, and tomographic results were analyzed at baseline and five days after treatment to assess the effect of umifenovir. Thirty (30) COVID-19 patients (mean age: 36.5 years [SD: 12.1, range: 19-59]), including 18 (60%) males and 12 (40%) females, were recruited for the study. There were no significant differences in age or gender, but there were significant differences in TTCR among the two categories. Body temperature (BT) and cough recuperation time [2.8 (0.6) and 2.6 (0.6) days, respectively] were highly reduced in the umifenovir category at 2.4 and 2.1 days, respectively. Moreover, many patients treated with umifenovir exhibited no side effects. In this study, pneumonia was ameliorated in 76.6% (23/30) of the patients, with moderate and potential amelioration in 36.6% and 40% of the patients, respectively. In addition, 66.6% of the patients in the umifenovir category had potential pneumonia absorption.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.