Abstract
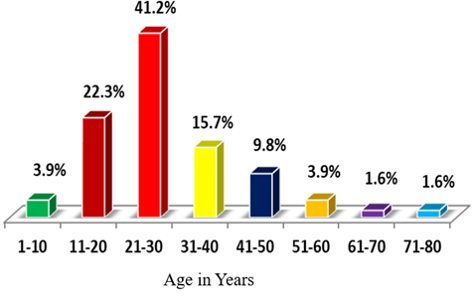
The main aim of the study is to evaluate the prescribing pattern of drugs prescribed in the ambulatory patients attending the dermatology department. This was a prospective observational study conducted for a period of 6 months. Patients who were receiving treatment in the dermatological outpatient department and willing to participate were included in the study and patients in the inpatient dermatology department and also with other co morbid conditions were excluded from the study. A total of 306 cases were collected and among them, about 112 (36.6%) were males and 194 (63.4%) were females. During the study period, majority of the patients were in the age group of 21-30 years (41.2%). The most commonly prescribed classes were found to be Antibacterial drugs 312 (22.1%) followed by Antifungal drugs 258 (18.3%) and Anti-histamines 206 (14.6%). Among the antibacterial, Antibacterial soaps (35.3%) were more commonly prescribed followed by the antibiotics Mupirocin (12.8%) and Clindamycin (11.9%). In case of Anti- fungals, Ketoconazole (25.2%) was most commonly prescribed drug followed by Fluconazole (14%) and Clotrimazole (14%). Among the Antihistamine drug class, Levocetrizine (76.2%) was most commonly prescribed followed by Hydroxyzine (12.2%). The drug Prednisolone (26.4%) was most commonly prescribed among Corticosteroids, followed by Mometasone furoate (23.6%) and Hydroquinone (13.1%). It is the responsibility of the clinical pharmacist to perform the drug utilization studies in order to know the drug prescribing patterns and also to know the prevalent disease conditions at a particular point of time. Clinical pharmacist should create awareness regarding the personal and community hygiene which would result in the prevention of dermatological diseases.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.