Abstract
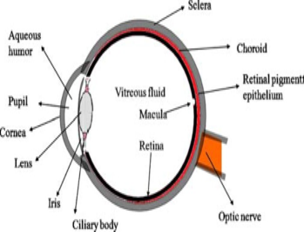
Eyes are considered as one of the most important organs of the body. The main hurdle for achieving effective ocular treatment is the maintenance of adequate quantity of drug at the site of action within the eye. Maintaining the concentration of drug in the eye is a difficult task as the anatomy and physiology of the eye leads to the draining of the drug from the eye. This leads to poor ocular bio availability and there by poor ocular therapy. The ocular bio availability can be improved by increasing the ocular retention time of the formulation. Insitu gel formation technology is a promising technique to prevent the lacrimal drainage of the drug rapidly from the eyes. Insitu gel preparation will be in liquid from when prepared, they are administered into the Cul-de-sac of the eye. Due to the environmental characteristics of the eye such as temperature, pH, Ionic concentration etc. the liquid formulation changes to gel form. This will increase the residence time and contact time of the drug with the mucosa of the eye. Insitu gels can increase the ocular bioavailability of the drug .The primary requirement of a successful control release product focuses on increasing patient compliance, good stability and bio compatibility. Insitu gels are used now a days as vehicles for both local and systemic drug therapies. This review deals with the study of a novel insitu gel approaches as a means to localize and prolong drug activity at its site of action.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.