Abstract
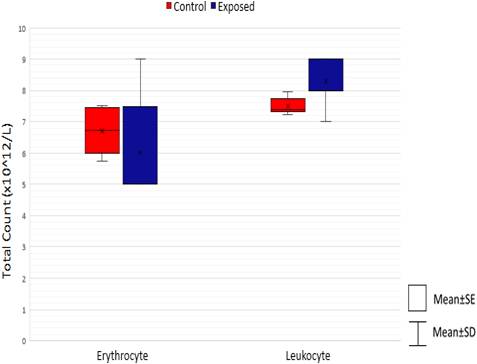
Exposure to microwave (MW) radiation causes a variety of changes in biological systems, including the hematopoietic and immune systems. This study was conducted to evaluate the effects of low-frequency MW radiation on erythrocytes and leukocytes in Sprague Dawley rats. Twelve male Sprague Dawley rats with an average body mass of 250 g were divided into control group (n=6) and exposed group (n=6). Rats in the exposed group were irradiated to 2.45 GHz MW radiation for eight weeks (five days a week, eight hours a day). Blood profile was then analyzed following completion of exposure regime. Findings of this study demonstrated that MW radiation expo- sure caused a significant increase in the total erythrocyte count, total leukocyte count and total differential count of lymphocyte, neutrophil, monocyte and eosinophil compared to the non-exposed group. In contrast, the basophil count was significantly decreased in comparison to control group. However, the mean corpuscular value (MCV), mean corpuscular haemoglobin (MCH) and mean corpuscular haemoglobin concentration (MCHC) values were not significantly affected by MW radiation exposure. For blood morphology, neutrophils exhibited an alteration in the cell where degradation of cytoplasm was observed, while lymphocyte, monocyte, basophil and eosinophil were found to be normal after exposure. In summary, exposure to MW radiation affects several haematological parameters and morphological changes which may pose deleterious negative health impacts.
Full text article
Generated from XML file
Authors
Syahidatul Asraf MS, Azlina M, Norazureen Nadhira Z, Qalidah MA, Izuddin Fahmy Abu, & Noor Ezati S. (2023). Effects of 2.45 GHz Microwave Radiation Exposure on Rat Erythrocytes and Leukocytes. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 9((SPL 2), 73–77. Retrieved from https://ijrps.com/home/article/view/4515
Copyright (c) 2018 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.