Abstract
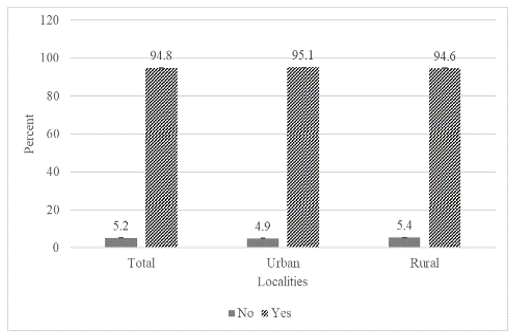
There is a growing interest on research related to health-seeking behaviours. However, there are minimal studies in Malaysia which focus on this issue. This paper aimed to determine the health-seeking behaviours among the Malay population and its association based on the localities of the urban and rural population. To achieve this purpose, a cross-sectional survey was conducted using face-to-face interview method. A total of 480 respondents participated in this survey with the majority (57.7%) of them were from a rural area. Among all the subjects, 4.9% and 5.4% of urban and rural participants respectively, did not seek treatment when they were sick. The reasons being are they chose to ignore the pain (80%), time-consumption (8%), and they do not believe in modern treatments (8%). A higher number of rural participants chose public healthcare facilities compared to urban (82.3% vs 72.6%, p<0.001), whereas a higher number of urban participants chose private healthcare facilities in contrast to rural participants (25.3% vs 16.4%, p<0.001). For participants with chronic diseases, 5.3% did not go for follow-up, 91.2% rely on healthcare staffs for information on the diseases, and 18.9% took traditional or supplementary medicine. Majority of the participants are in agreement that the accessibility to public healthcare facilities in terms of distance, transportation and operational time, as well as the services to get treatments, were good. However, there is a small number of participants who did not seek for treatments, including those with chronic diseases.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.