Abstract
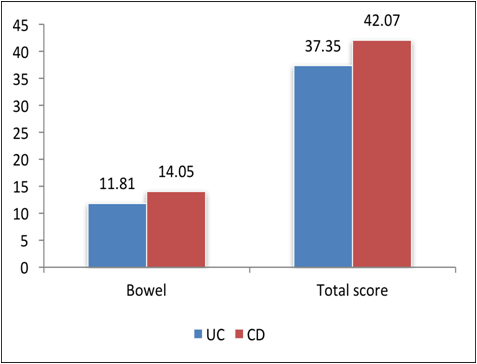
Assessment of health-related quality of life among Iraqi inflammatory bowel disease patients as well as assess the effects of sociodemographic and clinical variables on health-related quality of life. The current cross-sectional study was carried out on 150 patients already diagnosed with inflammatory bowel disease who attended the Gastrointestinal and Hepatology Teaching Hospital/Medical City/Baghdad. The mean age of the patients was (31.7 ± 11.4 years), the number of Crohn's disease patients was 76 while the number of ulcerative colitis patients was 74. Total health-related quality of life score was significantly higher in Crohn's disease compared to ulcerative colitis. Regarding the components of health-related quality of life: only bowel score was significantly higher in Crohn's disease compared to ulcerative colitis. For all patients, higher education levels, out-patient management, and a higher number of infliximab doses received predict the high health-related quality of life (direct correlation). For ulcerative colitis patients, patients received treatment in an outpatient setting, and a higher number of infliximab doses predict the high health-related quality of life (direct correlation). For Crohn's disease patients, in univariate analysis; patients received treatment in an out- patient setting, predict the high health-related quality of life (direct correlation), while a higher number of chronic drugs inversely correlate with health-related quality of life. Health-related quality of life total score and the bowel score were significantly higher in CD compared to UC. For all patients, higher education levels, out-patient management, and a higher number of infliximab doses received predict elevated HRQOL.
Full text article
Generated from XML file
Authors
Nisreen Jumaah Jebur, Dheyaa J. Kadhim, Nawal M. Firhan, & Hayder Adnan Fawzi. (2018). Assessment of health-related quality of life of Iraqi patients with inflammatory bowel disease. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, 9(3), 714–720. Retrieved from https://ijrps.com/home/article/view/4331
Copyright (c) 2018 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.