Abstract
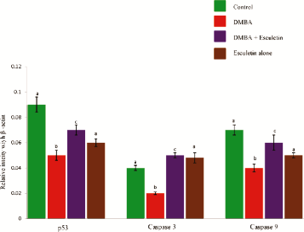
Evasion of apoptosis has been recognized as one of the salient features of the tumour cell. The programmed cell death is regulated by a spectrum of apoptotic proteins, which include both pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic markers. The aim of the present study is to explore the apoptotic induction potential of esculetin by analysing the expression pattern of apoptotic markers in 7,12- dimethylbenz(a)anthracene (DMBA) - induced oral carcinogenesis. Tumours were developed in the hamster’s buccal mocosa using a site-specific carcinogen, DMBA [topical application, 3 times a week for 14 weeks]. While the buccal mucosa from the hamster treated with DMBA alone (tumour bearing hamster) exhibited abnormal pattern of apoptotic markers (p53, Bcl-2, Bax, caspase 3 and caspase 9), the expression pattern was found to be reverted to near normal pattern in DMBA+esculetin treated hamster’s buccal mucosa. The present results thus reveal the esculetin ability to induce apoptosis in DMBA-induced hamster buccal pouch carcinogenesis.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.