Abstract
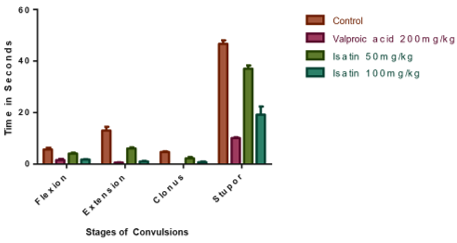
Anticonvulsant activity was determined after per oral administration of the isatin derivative in albino wistar mice by maximal electroshock (MES) induced seizure method in rats. The acute anticonvulsant effect of the derivative is compared with the standard drug Valproic acid. Control, standard and isatin derivative was injected throughout the experimental period for seven days. On the 7th day, animals were subjected to MES induced convulsions by electroconvulsometer by the application of electrical current to the brain via corneal electrodes and observed their behavior for 30 minutes. Abolition of the hind limb tonic extensor spasm was recorded as a measurement of anticonvulsant activity. The result showed that the isatin derivative at the dose of 50mg/kg depicted significant anticonvulsant activity as compared to control, while the dose of 100mg/kg elicited significant activity comparable to standard drug in reducing the duration of tonic hindleg extension and in decreasing the percent mortality.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.