Abstract
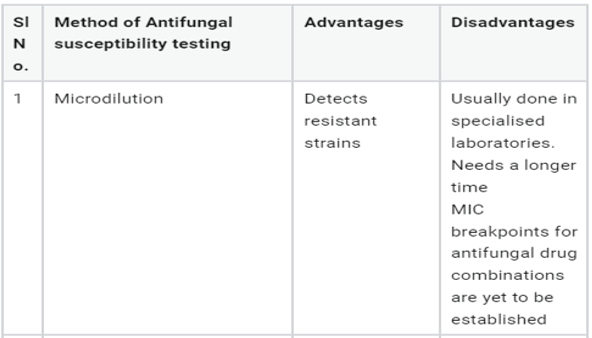
Despite the availability of many antifungal drugs in clinical practice, the occurrence of antifungal drug resistance is on the rise. Since the antifungal susceptibility testing (AFST) is not done routinely in many of the microbiology laboratories, it is very difficult to determine which antifungal agent is very effective for a particular infection. There is a real need for precise, reproducible and extrapolative antifungal susceptibility testing methods to aid the therapeutic management. The practice of empirical treatment for fungal infections further promotes the emergence of resistant strains. The AFST practice would essentially help the clinicians in appropriate decision making. Although conventional AFST methods are somewhat cumbersome, many novel AFST methods are currently available in many laboratory settings which would provide a quicker result many times. In essence, the application of AFST along with identification of the fungus up to species level would definitely be very helpful in selecting the primary antifungal agents for treatment especially in difficult to manage and invasive fungal infections. This review will throw light on the various AFST methods available and their issues in the current practice.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.