Abstract
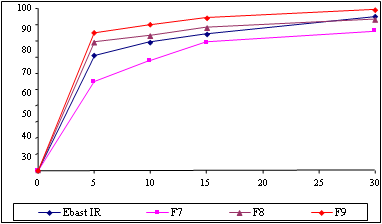
Ebastine is a second generation antihistamine mainly used for allergic rhinitis and urticaria. Ebastine is available in India as a conventional immediate release tablet; there is a need of formulating Ebastine in mouth dissolving tablet form to allow the administration of the dosage form without water, where particularly important for geriatrics, pediatrics and mentally retarded patients. Since, Ebastine is insoluble in water, different formulation techniques and excipients were tried for formulation of mouth dissolving tablets, molecular dispersion granulation technique was employed to optimize the formulation. Results were observed that, formulated mouth dissolving tablets are ready to disperse on tongue within a minute and the dissolution is very quick compared to the conventional immediate release tablets. Main physical parameters like weight variation, hardness, friability, fineness of dispersion and disintegration time and chemical quality parameters like assay and dissolution were evaluated during manufacturing and found satisfactory with meeting the pharamacopoeial limits. Finalized formulation F13 was packed in to blisters and charged for stability at 40°C/75%RH. Main physical and chemical quality parameters were evaluated during stability and found satisfactory. Dissolution profile was also generated during stability showed satisfactory results compared to initial dissolution profile.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.