Abstract
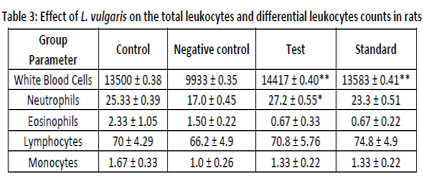
Fresh juice of Lagenaria vulgaris has been prescribed traditionally for the treatment of pain, gastric ulcer, fever, pectoral cough, asthma, treatment of inflammation and hepatotoxicity. L. vulgaris is known to contain actives like triterpenoid cucurbitacins B, D, G, H, fucosterol, campesterol, flavone C-glycosides, various antioxidants like ascorbic acid and β-carotene which are reported to have therapeutic efficacy. In the present work, fresh juice of L. vulgaris was evaluated for its in-vivo antioxidant and immunomodulatory activity against pyrogallol induced immunosuppression. For in-vivo antioxidant activity, various parameters such as lipid peroxidation, reduced glutathione, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase were evaluated as markers of oxidative stress. Specific immune responses including humoral (both primary & secondary) and cellular immune response were determined. Phagocytosis, total leukocyte count and differential leukocyte count as a measure of non specific immunity were also estimated. It was observed that juice of L. vulgaris showed stimulation of both humoral and cellular immune responses in immunocompromised conditions. There was increase in neutrophils and total leukocyte count, which could be responsible for stimulation of non-specific immunity, mediated by phagocytosis and delayed type hypersensitivity (DTH) response. Thus fresh juice of L. vulgaris showed significant protection against oxidative stress induced immunosuppression by pyrogallol.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.