Abstract
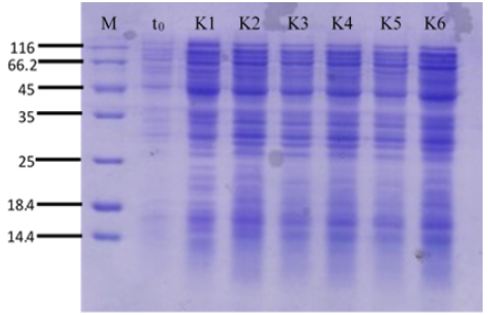
Human serum albumin (HSA) is the most abundant protein in blood plasm. This protein consisted of 585 amino acids with a molecular weight of 66 kDa and 17 disulfide bonds. HSA obtained from conventional technique allow viral or prion contamination. For that reason, recombinant DNA technology becomes a promising alternative. Because of its well-known genetic, simplicity, and capacity to accommodate many foreign protein, Escherichia coli remains the most widely used in the production of recombinant proteins. But, overproduction of protein may lead to the formation of inclusion bodies and proteolytic degradation. These problems can be overcome by using protease-deficient strain and protein secretion into periplasmic space. The objective of this research is to secrete recombinant HA on E. coli BL21(DE3) using TorA signal peptide and proved using SDS-PAGE. This research method begins with the preparation of competent cell and transformation of E. coli BL21(DE3), expression of recombinant HA in E. coli BL21(DE3), and characterization of expression result by using SDS-PAGE. The result of this study was rHSA can be secreted into extracellular medium using TorA signal peptide with a molecular weight of ± 66.5 kDa.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.