Abstract
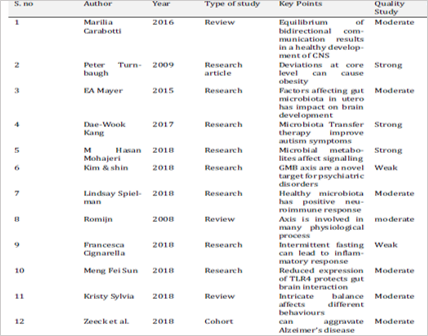
The gut brain axis is a bidirectional system which is highly complex and fragile and is an integral part of the functioning of the human body as it develops the human being. There are various diseases, disorders and factors revolving around this axis and this review looks into said factors. This axis is highly sensitive and is known to play a key role in the development of the brain as well as in the development of disorders such as obesity, depression, diabetes, autoimmune disorders and anxiety among others.The primary component of this axis is the gut microbiota.Its postulated that Gut microbiome can promote and aggravate neurogenerative disorder.Impact of core microbiome on the gene level affects the metabolism. The aim of the study is to analyse the impact made by the studies analysed in this report. 35 articles were taken from various databases and were reviewed for their effect on the topic. This study reviews the articles that discuss the various effects of the gut brain axis. These articles when studied together point at the same fact that there is a lot of potential in this field. This review is an attempt to update recent advancements in Gut-Brain axis, further research is in need of the hour about its complete use to humanity.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.