Abstract
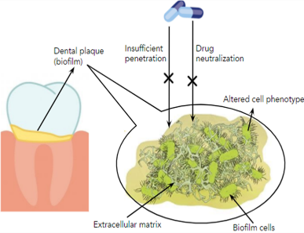
Bacterial biofilm has been a major contributor to severe bacterial infections in humans. Oral infections have also been associated with biofilm-forming microbes. Several antimicrobial strategies have been developed to combat bacterial biofilms. However, the complexity of the oral cavity has made it difficult to use common drug treatments. Most effective ways to control normal bacterial infections are rendered ineffective for bacterial biofilms. Due to limited drug concentration availability, drug neutralization or altered phenotype of bacterial cells, different drug have been ineffective to identify the target cells. This leads to the development of the multifaceted phenomenon of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Biofilm research done so far has been focused on using antimicrobial drugs to target molecular mechanisms of cells. The severity and resistance mechanisms of extracellular matrix (ECM) have been underestimated. The present study describes different antimicrobial strategies with respect to their applications in dental or oral infections. A prospective strategy has been proposed targeting ECM which is expected to provide an insight on biofilm obstinacy and antimicrobial resistance.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.