Abstract
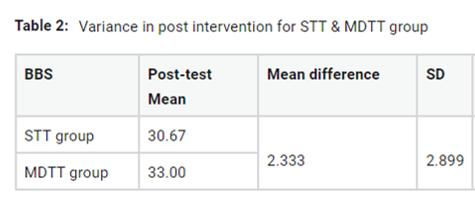
The motivation of investigation was to discover the impact of motor dual task training (MDTT) vs single task training (STT) on useful parity in post stroke patients. Thirty first beginning of one-sided ischemic “Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA)” domain stroke patients are haphazardly designated into 2 gatherings the STT gathering (n=15) got single task strengthening and balance practices and MDTT (n=11) got strengthening & balance practice alongside an optional engine task. Intercession is provided 45 minutes for every session, once in a day, 5 days of week for about fourteen days. The parity was dissected utilizing Berg Balance Scale (BBS). In 2 groups, balance expressively enhanced in BBS. Compared with STT group; MDTT group reached much statistically important development. The MDTT exercises efficiently promote balance initial in stroke patients. How parity is influenced relies upon a few variables, comprising the degree of sensory system harm, the number and degree of tactile misfortunes, and the accessibility of different faculties for pay. In numerous occurrences, greater than one tactile framework is hindered.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.