Abstract
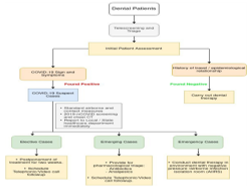
Coronavirus outbreak (2019-nCoV) emerged as a global health threat. World Health Organization (WHO) unveiled it as an international emergent situation. 2019-nCoV person-to-person transmission typically occurs through coughing, sneezing, droplet inhaling, and surface touch. Containment measures are needed to prevent further spread. It is worth mentioning that the risk of cross-infection among patients and dentists are high as oral investigations and treatment measures involve one-on-one contact, exposure to blood, saliva, and other bodily fluids. Therefore, effective countermeasures shall be planned to inhibit 2019-nCoV transmission in the dental setting as well. This review article highlights the essential knowledge of possible transmission routes of 2019-nCoV in dental settings. It also focuses on effective practice to be followed by dental health care practitioners (DHCP) to block the routes of transmission in dental clinics and hospitals. The article also attempts to highlight future challenges involved in a dental setting in India. This review will be especially helpful for dentists and maxillofacial in following the informed guidelines to prevent the spread of coronavirus disease (COVID-19).
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.