Abstract
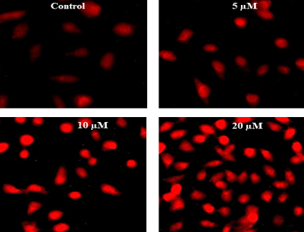
Sclareol, a labdane diterpene phytochemical in the various genus Salvia of the herbaceous plant has been anti-carcinogenic properties on numerous human cancer cell lines. Till known the anticancer properties of sclareol on human oral KB cancer cells are not revealed. Therefore, we scrutinized the viability, nucleate damage associated with apoptosis in KB cells treated with sclareol. The cytotoxicity of KB cells displayed to sclareol was evaluated by hexosaminidase and trypan blue exclusion assay. Apoptosis was noticed by Hoechst staining and affirmed by nucleate damage. We discovered that sclareol treatment for KB cells with expressively lessened cell proliferation or viability and evoked cell death in a dose-dependent manner compared with untreated control. Sclareol stimulated inhibition of growing of oral KB cells came along to be induction nucleate damage. Our data proved that sclareol on stimulated apoptosis in human oral KB cancer cells through nucleate damage. These observations recommend the anti-cancer properties of sclareol.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.