Abstract
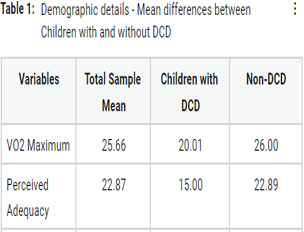
A characteristic hallmark motor in proficiency marks developmental coordination disorder (DCD). Children with DCD have low confidence in their physical abilities and lower perceived self-efficacy toward physical activities than their age-matched peer-group children without DCD. The study aims to evaluate aerobic fitness among children diagnosed with Developmental Coordination Disorder and to examine whether their lies any individual differences among children, who were suspects of DCD. Twenty children were enrolled in after baseline examination as DCD using DCDQ. Each child completed 6 Minute Walk test and Children’s Self-perception of Adequacy in and the predilection for Physical Activity (CSAPPA). When considering the individual differences among children with DCD, there occurs a different result and cardiovascular fitness trend in children with DCD. Fitness is related to the self-perception of ability among children. This study provides evidence that self-perception ability among children is an essential component that needs to be considered when planning therapeutic intervention to enhance cardiovascular fitness in children with DCD.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.