Abstract
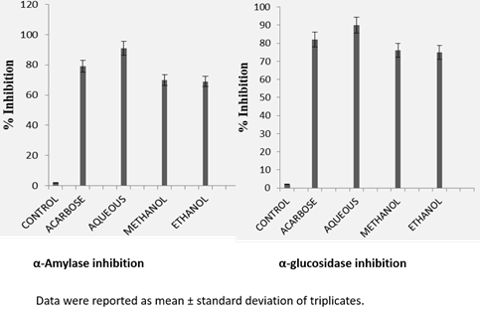
The main objective of the present study was to investigate the nutraceutical properties of the bioactive components from the extracts of Canthium parviflorum seeds (CPS). The anti-oxidant property of CPS extracts was carried out by estimating the total phenolic, flavonoid contents, flavonols, flavonols and radical scavenging properties. The results of these findings show that the aqueous extract of CPS rich in polyphenols (87.5 ± 0.2 mg GAE /g) and flavonoids (50.1 ± 0.2 mg QE/g) compounds than organic extracts. The effective inhibitory activity of CPS against α- amylase and α- glucosidases enzyme related to type- 2 diabetes was evaluated and compared. The aqueous extract was exhibited the maximum α-amylase and β-glucosidase inhibition of 91.1 ± 0.4 and 90.5 ± 0.1 % respectively. The seed extracts show a maximum of 25.5 % of protein and 6.4 mg/100g of zinc. The seed extract was exhibited maximum anti-oxidant property with beta carotene content of 5.4 mg/100 g of seed. The present work may be the platform to use to develop highvalue nutritional compounds by unutilized plant materials. The natural anti- oxidant and polyphenols present in the extracts were showed great nutraceutical value, and it may be used to develop nutraceutical to enhance a healthy diet.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.