Abstract
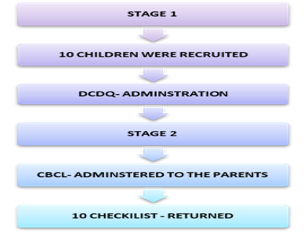
Motor task execution capability again included in the writing task. The ability of the child to copy down the letters from the blackboard and the ability to listen to the dictated word and coordinate the writing task along with the listening task to complete the note-taking process. Lack of motor task execution capability will exclude the child from green land play. Playing demands attention skill as well as motor co-ordination. We aimed to compare the level of attention among children with and without DCD during their functional activities that demand motor performance. Ten children with and without DCD were included in the study. Their motor performance was assessed with the Movement Assessment Battery for Children (MABC), and a self-reported questionnaire evaluated attention during the tasks of the MABC. All children with DCD had higher MABC impairment scores and lower attention scores than their peers. It has been documented that children with DCD were less attentive to movements than their peers, and the positive reinforcement can modulate their performance by the parents or therapist.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.