Abstract
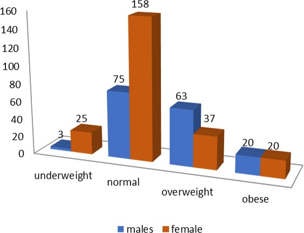
As defined by the World Health Organisation (WHO), physical activity is any bodily movement produced by skeletal muscles that require energy expenditure. Physical activity is split into exercise and non-exercise physical activity. Physical inactivity is associated with many chronic and non-communicable diseases such as hypertension, type II diabetes mellitus, carcinoma and mental health problems. According to the global statistical report of WHO, around 1.6 million deaths occur annually, and these deaths can be attributed to insufficient physical activity. This study would aim to assess the practice of physical activity among medical students and to study the factors associated with physical activity. A cross-sectional study was conducted in a private medical college between January 2020 and March 2020, 444 undergraduate students were included in the study, among which 401 responses were considered valid. A standard international physical activity questionnaire (IPAQ) was used. The data were entered in Microsoft Excel and analysed using Pearson’s chi-square test. The students belonged to 1st year 125(31.2%), 2nd year 128(31.9%), 3rd year 133(33.2%) and 4th year 15(3.7%). Majority of these students 233(58.1%) had an average Body Mass Index (BMI) and 184(45.9%) practised low level of physical activity. In comparison with the level of physical activity, batches (1st year, 2nd year, 3rd year, 4th year) and gender(males, females) were significant at p<0.05, but BMI was not significant at p<0.05. Comparing the level of physical activity with the BMI of the students, it can be concluded that the level of physical activity is not associated with BMI.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.