Abstract
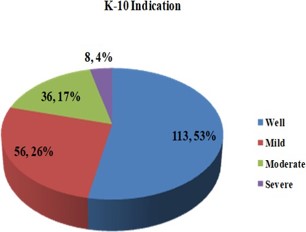
An elevation in blood pressure is an important risk factor of cardiovascular disease and several factors that can contribute to hypertension induce psychological distress. This study was aimed at estimating the prevalence of psychological distress and to assess general awareness regarding disease, concomitant substance abuse, and use of herbal drugs among hypertensive patients (HTN-Pt) at Satguru Pratap Singh (SPS) Hospitals, Ludhiana. The psychological distress was assessed using the standard Kessler-10 scale along with face-to-face interview among 275 outpatient department (OPD) HTN-Pt on follow-up. 15.30% (n=33) of total participants (n=213) had alcohol use disorders and 8.80% (n=19) of them were addicted to smoking habits. K10 scale results in patients, showed 46.9% (100) patients were suffering from psychological distress out of which 26% (n=56) were having mild, 17% (n=36) moderate and 4% (n=8) patients were having severe psychological distress. Highest percentage (33.80%) of patients with psychological distress were from age group 31-60 years of age (p value=0.003, COR= 0.240, 95% CI 0.072, 0.584). Many HTN-Pt were consuming the herbal supplements out of which 92 % of patients consuming grapes were found to have psychological distress (p value=0.034, COR= 0.380, 95% CI 0.155, 0.930). The results of the study indicated that there was a high prevalence of psychological distress in HTN-Pt belonging to age group of 31-60 years of age and patients involved in the consumption of grapes. This study asks for supervision on the concomitant administration of herbal supplements with allopathic medicines in HTN-Pt to avoid psychological distress.
Full text article
References
Awuah, R. B., de Graft Aikins, A., Dodoo, F. N.-A., Meeks, K. A., Beune, E. J., Klipstein-Grobusch, K., Addo, J., Smeeth, L., Bahendeka, S. K., Agyemang, C. 2019. Psychosocial factors and hypertension prevalence among Ghanaians in Ghana and Ghanaian migrants in Europe: The RODAM study. Health Psychology Open, 6(2):1–9.
Bahar, Z., Kizilci, S., Beser, A., Besen, D. B., Gördes, N., Ersin, F., Kissal, A., Çapik, C. 2013. Herbal therapies used by hypertensive patients in Turkey. African Journal of Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines, 10(2):292–298.
Bissa, S., Mossie, A., Gobena, T. 2014. Prevalence of hypertension and its association with substance use among adults living in Jimma Town South West Ethiopia 2012. World Journal of Medicine and Medical Science, 2(1):1–11.
Cuffee, Y., Ogedegbe, C., Williams, N. J., Ogedegbe, G., Schoenthaler, A. 2014. Psychosocial Risk Factors for Hypertension: an Update of the Literature. Current Hypertension Reports, 16(10):483.
Edwards, Q. T., Colquist, S., Maradiegue, A. 2005. What’s Cooking with Garlic: Is This Complementary and Alternative Medicine for Hypertension? Journal of the American Academy of Nurse Practitioners, 17(9):381–385.
Footman, K., Roberts, B., Tumanov, S., McKee, M. 2013. The comorbidity of hypertension and psychological distress: a study of nine countries in the former Soviet Union. Journal of Public Health, 35(4):548–557.
Go, A. S., Mozaffarian, D., Roger, V. L., Benjamin, E. J., Berry, J. D., Blaha, M. J., Dai, S., Ford, E. S., Fox, C. S., Franco, S., Fullerton, H. J., Gillespie, C., Hailpern, S. M., Heit, J. A., Howard, V. J., Huffman, M. D., Judd, S. E., Kissela, B. M., Kittner, S. J. 2014. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2014 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation, 129(3):e28–e292.
Gupta, R., Gaur, K., Ram, S., Venkata, C. 2019. Emerging trends in hypertension epidemiology in India. Journal of Human Hypertension, 33(8):575–587.
Hamer, M., Batty, G. D., Stamatakis, E., Kivimaki, M. 2010. Hypertension awareness and psychological distress. Hypertension, 56(3):547–550.
Hu, B., Liu, X., Yin, S., Fan, H., Feng, F., Yuan, J. 2015. Effects of Psychological Stress on Hypertension in Middle-Aged Chinese: A Cross-Sectional Study. PLOS ONE, 10(6):e0129163.
Muammar, M. A. A., Alsubaihi, I. A., Alqahtani, M. K. S., Dajam, H. S., Alshanqiti, O. A. M., Darwish, N. B. B., Alrakha, A. M., Aloufi, R. F., Alyami, M. R. H., Alanazi, S. F. 2019. Evaluation of Recent Updates Regarding the Management of Resistant Hypertension. Archives of Pharmacy Practice, 10(3):65–70.
Nandhini, S. 2014. Essential Hypertension - A Review Article. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 6(9):305–307.
Ojike, N., Sowers, J. R., Seixas, A., Ravenell, J., Rodriguez-Figueroa, G., Awadallah, M., Zizi, F., Jean-Louis, G., Ogedegbe, O., Mcfarlane, S. I. 2004. Psychological Distress and Hypertension: Results from the National Health Interview Survey for 2004-2013. Cardiorenal Medicine, 6(3):198–208.
Soboka, M., Gudina, E. K., Tesfaye, M. 2017. Psychological morbidity and substance use among patients with hypertension: a hospital-based cross-sectional survey from South West Ethiopia. International Journal of Mental Health Systems, 11(1):5.
Ugwu, D. I., Onyedibe, M. C. C., Chukwuorji, J. B. C. 2021. Anxiety sensitivity and psychological distress among hypertensive patients: the mediating role of experiential avoidance. Psychology, Health and Medicine, 26(6):701–710.
Wong, M. K., Darvishzadeh, A., Maler, N. A., Bota, R. G. 2016. Five Supplements and Multiple Psychotic Symptoms: A Case Report. The Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders, 18(1).
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.