Abstract
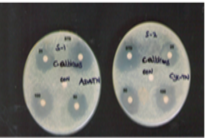
Identification of a novel antimicrobial molecule is vital to research due to contaminated agro related products and harmful pathogens. Especially, candida albicans is the most common infective fungi in the world that causes hospital-acquired infections. There is a medical and biological need for the discovery of novel antimicrobial drugs with high potent in nature. This effort involves the synthesis of scaffold molecule in which vitamin B3 and oxazole play vital role as pharmacophore moiety, where 2-(Nicotinamido) oxazole-4-carboxylic acid couples with pyridine–3-carboxylic acid (nicotinic acid) and 2-aminooxazole derivatives. Then, it is carried for mass spectra, 1H NMR spectroscopy, and growth control ability study against microbial targets such as fungi and bacteria. The zone of inhibition is measured in millimeters for the serially diluted solution of the compound. From the outcomes, the compound (5i) displayed 35mm of inhibition zone area, but standard fluconazole showed 29mm for 250 ppm solution. The outcome revealed that the amide bond and oxazole moiety turn as imperative pharmacophore besides showing decent inhibition activities.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.