Abstract
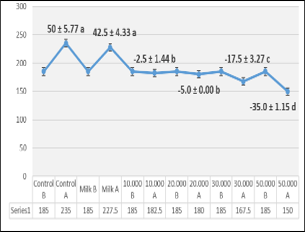
The research was undertaken to evaluate the effects of vitamin D3 on the liver and kidney functions through some haematological and biochemical parameters. The results illustrate that high doses (30000 and 50000 IU) of vitamin D3 significantly reduce the rats' body weights in about 46% additionally much of symptoms like weakness, the rigidity of limbs, neurological irritation, difficulty in movement, respiration and deaths occurrence. The results also showed that the high doses vitamin D3 has a significant decreased in Red Blood Corpuscles (RBCs), Hemoglobin (Hb), Packed Cell Volume (PCV), Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV), Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH), White Blood Corpuscles (WBCs), Lymphocytes (Lymph), Monocytes (Mono), Granulocytes (GRA) and Platelets (PLT) compared with the control group. In contrast, the Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC) and Platelet Distribution Width (PDW) significantly increased after 20-30 days of treatment. Besides, the results demonstrated a significant decrease in Alanine aminotransferase (ALT), Total Protein (TP), Creatinine (Cr) and increase in aspartate aminotransferase (AST), Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN), Urea. While albumin did not give any significant differences. As well the study proved significantly increase in serum vitamin D3 concentration compared with the control group after 20-30 days of treatment. Since vitamin D3 can be beneficial for the organisms, but the overdoses of the vitamin can alter some parameters in the body.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.