Abstract
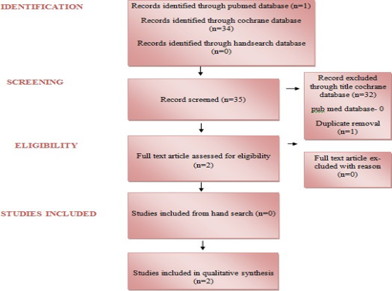
Third molar extraction is one of the most commonly performed minor surgical procedure in any dental practice worldwide, often accompanied by various postoperative sequelae such as swelling pain and trismus which intern affects the quality of life of a patient. Over the past few decades, different methods have been proposed in the literature and were clinically evaluated to reduce the postoperative discomfort after mandibular third molar impaction and out of which corticosteroids, have shown promising results. Dexamethasone (administered either orally, submucosally, IV or IM), methylprednisolone acetate and methylprednisolone sodium succinate (IV or IM or submucosal) are most commonly preferred corticosteroids in oral and maxillofacial surgery. The main objective is to systematically review the comparison of the effectiveness of submucosal administration of dexamethasone with methylprednisolone following mandibular third molar impaction in reducing the postoperative sequelae, and its discomfort and searches were performed in the PubMed, Medline, Scopus, and Cochrane Library databases. Two articles were most relevant, and the results of the comparison of the selected articles were analysed. From this deliberate audit, it is very well may be inferred that submucosal injection of dexamethasone plays a promising role in reducing the postoperative sequelae which includes swelling, pain and trismus and its discomfort following mandibular third molar impaction when compared with that of methylprednisolone.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.