Abstract
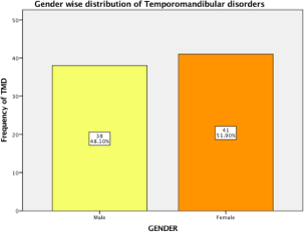
Temporomandibular joints (TMJ) are the bilateral synovial articulation between temporal bone and lower jaw, seen on each side of the jaws. Temporomandibular joint disorders (TMD) can be defined as the tenderness of the jaws and dysfunction of the associated muscles of mastication and the temporomandibular joints, which connect the mandible to the skull. The exact cause of TMD still remains mysterious and unclear. However, the possible attributes of TMD are arthritis, trauma or blow to the TMJ, excessive gum chewing and bruxism. Patients are usually treated with ice packs, gentle massage at the jaw area and prescription of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). This study sought to evaluate the incidence rate, age and gender differences of TMD among patients reporting to Saveetha Dental College and Hospital. The following parameters were evaluated based on the dental records; age, gender and types of TMD. Excel tabulation and SPSS version 23 was used for data analysis. The prevalence of temporomandibular disorders was higher in female patients (51.9%) than male patients (48.1%). The most frequent age group affected by temporomandibular disorders was 31-40 years (36.7%). Disc-condyle disorder (75.9%) is the most frequent sub-type of temporomandibular disorders present in the patients. There was no statistically significant correlation between age and TMD (p=0.847); and gender and TMD (p=0.365). It can be concluded that within the limits of study, TMD was present in adulthood and was more common in women, with disc-condyle disorder being the most prevalent type.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.