Abstract
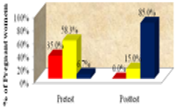
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is an infection that assaults immune cells called CD4 cells, which are a kind of T cell. These are white platelets that move around the body, recognizing flaws and inconsistencies in cells just as contaminations. The present study aimed to effectiveness of interventional package on knowledge and attitude towards prenatal HIV testing and parent to child transmission among pregnant women in selected settings.60 pregnant women sample in Quantitative approach with Pre experimental one group pre-test and post-test design, sample selection was done by Non Probability – Purposive Sampling Technique, Effectiveness of structured teaching programme in meaning pregnant women gained 35% etiology and effects gained 31% in management and precautions in PCT pregnant women gained 41% prevention 36.8% overall they gained 37.28% and Attitude gained 23.3% after intervention. Pre-existing knowledge was assessed by using semi structured teaching programme, pregnant mothers gained 23.3% more knowledge score than pretest score and the mean difference is 12.80 by using generalized McNamara’s chi-square test, it is statistically significant. In pretest, mothers were having 10.77score whereas, in post-test they were having 23.57 score. Difference score is 12.80.The difference is large and it is statistically significant. Successful intervention toward prevention of mother-to-child transmission (PMTCT) and achieving the goal of eliminating the new HIV infection is highly dependent on everyone; especially, women of child-bearing age should have accurate and up-to-date knowledge about HIV transmission, risk of transmission to babies, and possible interventions.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.