Abstract
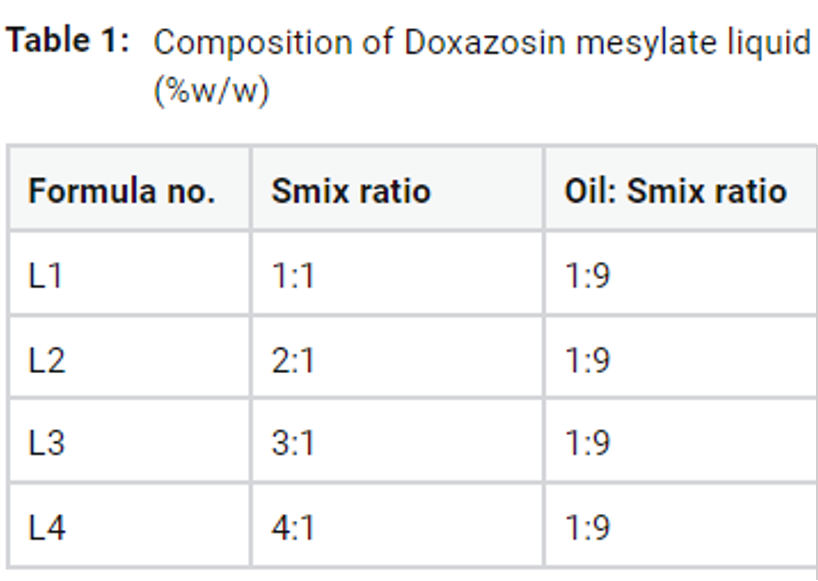
Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) in both liquid and solid forms were suggested to improve water solubility of Doxazosin mesylate (DOX) a poorly water- soluble antihypertensive drug. Oleic acid: Smix (1:9 w/w) and Tween 80: co-surfactant mixture (Ethanol and PEG 400) (1:1, 2:1, 3:1 and 4:1) were chosen to prepare a liquid and solid forms of SNEDDS according to their solubility. TEM images revealed change in the crystalline nature of DOX into uniform particles with smooth surface. Characterization studies revealed droplet size ranges from 79.80±14.39 to 273.10±4.17 nm, zeta potential ranges from -5.57±0.10 to -21.13±0.46 mV and dissolution enhancement of more than two folds with more favorable properties for the solid forms. FTIR demonstrated significant physical changes in DOX crystalline structure. In conclusion, the solid SNEDDS containing oleic acid: Smix (1:9 w/w) and Tween 80: co-surfactant mixture (3:1 w/w) and adsorbent mixture of Avicel 101 and Aerosil 200 (40:1 w/w) might be a promising formula for better management of hypertension with expected shelf stability.
Full text article
References
Ahmad, M., Sahabjada, J. A., Hussain, A., Badaruddeen, M. A., Mishra, A. 2017. Development of a new rutin nanoemulsion and its application on prostate carcinoma PC3 cell line. EXCLI journal, 16:810–823.
Aiswarya, G., Reza, K., Rajan, R. 2015. Development, evaluation, and optimization of flurbiprofen nanoemulsions gel using quality by design concept. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutics, 9(1):35–35.
Ali, H. H., Hussein, A. A. 2017. Oral solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems of candesartan citexetil: formulation, characterization and in vitro drug release studies. AAPS Open, 3(1):1–17.
Balata, G. F. 2018. Formulation and evaluation of gliclazide in vegetable oil-based self-emulsifying delivery system. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science, 8(09):23–033.
Balata, G. F., Essa, E. A., Shamardl, H. A., Zaidan, S. H., Abourehab, M. A. 2016. Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems as a tool to improve solubility and bioavailability of resveratrol. Drug design, development and therapy, 10:117.
Bhagat, C., Singh, S. K., Verma, P. R. P., Singh, N., Verma, S., Ahsan, M. N. 2013. Crystalline and amorphous carvedilol-loaded nanoemulsions: formulation optimisation using response surface methodology. Journal of Experimental Nanoscience, 8(7- 8):971–992.
Cherniakov, I., Domb, A. J., Hoffman, A. 2015. Self-nano-emulsifying drug delivery systems: an update of the biopharmaceutical aspects. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery, 12(7):1121–1133.
Cho, H. Y., Kang, J. H., Ngo, L., Tran, P., Lee, Y. B. 2016. Preparation and Evaluation of Solid- Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery System Containing Paclitaxel for Lymphatic Delivery. Journal of Nanomaterials, pages 1–14.
Chung, Vashi, Puente, Sweeney, Meredith 1999. Clinical pharmacokinetics of doxazosin in a controlled release gastrointestinal therapeutic system (GITS) formulation. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 48(5):678–687.
Date, A. A., Desai, N., Dixit, R., Nagarsenker, M. 2010. Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems: formulation insights, applications and advances. Nanomedicine, 5(10):1595–1616.
Debnath, S. U. B. H. A. S. H. I. S., Satayanarayana, K. V., Kumar, G. V. 2011. Nanoemulsion-a method to improve the solubility of lipophilic drugs. Pharmanest, 2(2-3):72–83.
Du, L., Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Qi, C., Wolcott, M., Yu, Z. 2017. Preparation and Characterization of Cellulose Nanocrystals from the Bio-ethanol Residuals. Nanomaterials, 7(3):51–51.
Farooq, U., Tweheyo, M. T., Sjöblom, J., Øye, G. 2011. Surface Characterization of Model, Outcrop, and Reservoir Samples in Low Salinity Aqueous Solutions. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 32(4):519–531.
Ige, P. P., Bachhav, N. A., Mahajan, H. S., Nerkar, P. P., Gattani, S. G. 2013. Atorvastatin-Loaded Oleic Acid Nanoglobules for Oral Administration: In Vitro Characterization and Biopharmaceutical Evaluation. Current Nanoscience, 9(2):202–210.
Izham, M. N. M., Hussin, Y., Aziz, M. N. M., Yeap, S. K., Rahman, H. S., Masarudin, M. J., Mohamad, N. E., Abdullah, R., Alitheen, N. B. 2019. Preparation and Characterization of Self Nano-Emulsifying Drug Delivery System Loaded with Citraland Its Antiproliferative Effect on Colorectal Cells In Vitro. Nanomaterials, 9(7):1028–1028.
Kalepu, S., Nekkanti, V. 2015. Insoluble drug delivery strategies: review of recent advances and business prospects. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 5(5):442– 453.
Khames, A. 2019. Formulation and Characterization of Eplerenone Nanoemulsion Liquisolids, An Oral Delivery System with Higher Release Rate and Improved Bioavailability. Pharmaceutics, 11(1):40–40.
Larsen, A., Ogbonna, A., Abu-Rmaileh, R., Abrahamsson, B., Østergaard, J., Müllertz, A. 2012. SNEDDS Containing Poorly Water Soluble Cinnarizine; Development and in Vitro Characterization of Dispersion, Digestion and Solubilization. Pharmaceutics, 4(4):641–665.
Mardiyanto, M., Untari, B., Anjani, R., Fithri, N. 2020. Solid Self Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System (Solid SNEDDS) of Mefenamic Acid: Formula Optimization using Aerosil® -200 and Avicel ® PH-101 with Factorial Design. International Research Journal of Pharmacy, 11(2):25–31.
Nasr, A., Gardouh, A., Ghorab, M. 2016. Novel Solid Self-Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery System (S-SNEDDS) for Oral Delivery of Olmesartan Medoxomil: Design, Formulation, Pharmacokinetic and Bioavailability Evaluation. Pharmaceutics, 8(3):20–20.
Nazzal, S., Zaghloul, A. A., Khan, M. A. 2002. Effect of extragranular microcrystalline cellose on compaction, surface roughness, and in vitro dissolution of a self-nanoemulsified solid dosage form of ubiquinone. Pharmaceutical technology, 26(4):86–86.
Patel, K., Sarma, V., Vavia, P. 2013. Design and evaluation of Lumefantrine–Oleic acid self-nanoemulsifying ionic complex for enhanced dissolution. DARU Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 21(1):1– 11.
Savjani, K. T., Gajjar, A. K., Savjani, J. K. 2012. Drug Solubility: Importance and Enhancement Techniques. ISRN Pharmaceutics, 2012:1–10.
Tong, Y., Wang, Y., Yang, M., Yang, J., Chen, L., Chu, X., Gao., C 2018. Systematic development of self- nanoemulsifying liquisolid tablets to improve the dissolution and oral bioavailability of an oily drug, vitamin K1. Pharmaceutics, 10(3):96–96.
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.