Abstract
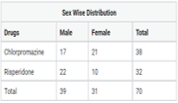
Patient safety is the foremost concern in the healthcare system. However, only a few studies have been conducted regarding the safety and efficacy of antischizophrenic drugs in the south Indian population. The main objective is to study relative safety profile and efficacy between chlorpromazine and risperidone among schizophrenia patients in teaching hospital. Prospective, observational, comparative study conducted for six months among schizophrenia patients. The data was collected from 62 enrolled subjects with the help of questionnaires and scales, and data was analyzed by using a t-test and other relevant descriptive analysis by using the statistical software SPSS version 20.0. Out of a total of 70 patients, males were 39, and females were 31. Out of 70 patients, only 62 patients completed the study according to the inclusion criteria. The occurrence of schizophrenia was higher in the age of late adolescence and early adulthood. Risperidone was more effective in treating negative and general symptoms compare to chlorpromazine, but equally efficacious in treating positive symptoms. Poor medication adherence was found in patients receiving both drugs. Chlorpromazine is more effective in a patient with predominantly positive symptoms. Risperidone is more effective and should be preferred in patients with positive, negative, and general symptoms.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.