Abstract
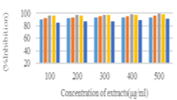
This study was conducted to assess the physicochemical analysis, qualitative and quantitative phytochemical analysis and antioxidant activity of various solvent (n-hexane, ethyl acetate, ethanol, and water) extract obtained from Trichodesma indicum aerial parts. The physicochemical analysis was carried out using standard reported methods. Successive solvent extraction was carried out using n-hexane, ethyl acetate, and ethanol by the Soxhlet method, followed by maceration with water. Qualitative phytochemical screening was done using standard procedures. The extracts were analyzed for its phenolic and flavonoid contents by Folin - ciocalteu and Aluminium chloride colorimetric methods. For the extracts, antioxidant activity was screened using three different methods, 1, 1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl assay, Nitric oxide assay, and Superoxide dismutase assay. Ascorbic acid has been used for antioxidant activity as a positive control. The percentage of inhibition was measured at various levels of concentration. The total ash, water-soluble ash, acid insoluble ash, sulfated ash, and the moisture content of the powdered drug was found to be 15.30, 07.50, 03.99, 21.00, 05.00%w/w. The qualitative phytochemicals found in the extracts are carbohydrates, proteins, and amino acids, flavonoids, phenols, phytosterols, saponins, tannins, and glycosides. The phenolic and flavonoid content of the extracts was found in the sequence of ethyl acetate ˃ n-hexane ˃ ethanol ˃ aqueous. All the extracts demonstrated significant concentration-dependent antioxidant activity in DPPH assay, Nitric oxide assay, and Superoxide dismutase assay. The findings indicated that all solvent extracts of Trichodesma indicum have promising antioxidant activity and that could be the presence of phytochemicals present in the extract.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.