Abstract
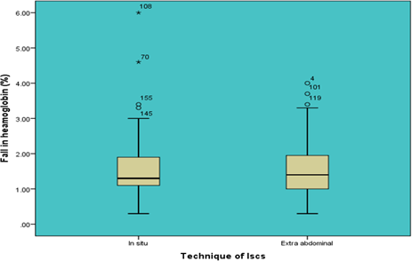
In-situ and extra abdominal repair of uterine wound during cesarean section are two valid approaches. This study was carried out to compare intra operative and post operative morbidity in women undergoing caesarean delivery using these two techniques. This is a prospective interventional randomized controlled study. The study subjects include 170 women undergoing Lower segment caesarean section (LSCS) at Southern Railway HQ hospital, Chennai. Intra operative and post operative parameters were analysed in all the study subjects. In in-situ group, 12.6 % women experienced intra operative pain and 30.1% women in extra abdominal group. Intra operative nausea and vomiting was seen in 16.1% women in in-situ group and 28.9% women in extra abdominal group. 1.1% women in in-situ had post-operative febrile morbidity and 8.4 % had in extra abdominal group. The median fall in haemoglobin was 1.30 g/dL and 1.40 g/dL in in-situ and extra abdominal group respectively. In-situ repair of the uterine wound at cesarean delivery is associated with lesser incidence of intra operative pain , intra operative nausea or vomiting and post operative febrile morbidity compared to extra abdominal repair technique.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.