Abstract
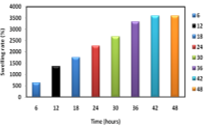
Hydrogels are 3D polymer networks capable to absorb and release water or biological fluids. They are stimuli-responsive materials, which can show rapid volume changes with response to small changes in environmental parameters such as ionic strength, pH, and temperature. In this work, we performed a synthesis of Poly(acrylamide) hydrogel and tested for controlled release of levofloxacin hemihydrate as a model drug. We used sodium metabisulfite and potassium persulphate as free radical initiators to prepare hydrogel with methylenebisacrylamide as a crosslinker. Characterization of hydrogel was performed by TGA, SEM, and FT-IR. Swelling study and drug release were performed at pH 1.2 and 7.4 solutions, identical to the gastrointestinal fluid at 37°C (human body temperature) to examine possible site-specific drug delivery. UV-Visible spectrophotometer was used to measure the concentration of drug release. Results exhibited the pH and temperature-dependent drug release. The amount of drug release was found to be 17% and 99% in acidic and alkaline pH of 1.2 and 7.4, respectively, after 6 hours.
Full text article
References
Anbarasan, R., Jayaseharan, J., Sudha, M., Gopalan, A. 2003. Sonochemical polymerization of acrylic acid and acrylamide in the presence of a new redox system? A comparative study. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 89(13):3685–3692.
Aouada, F. A., Chiou, B.-S., Orts, W. J., Mattoso, L. H. 2009. Physicochemical and morphological properties of poly(acrylamide) and methylcellulose hydrogels: Effects of monomer, crosslinker and polysaccharide compositions. Polymer Engineering & Science, 49(12):2467–2474.
Baishya, H., et al. 2017. Application of Mathematical Models in Drug Release Kinetics of Carbidopa and Levodopa ER Tablets. Journal of Developing Drugs, 6(2):1–8.
Chen, J., Liu, M., Liu, H., Ma, L. 2009. Synthesis, swelling and drug release behavior of poly (N, N-diethylacrylamide-co-N-hydroxymethyl acrylamide) hydrogel. Mater Sci Eng C, 29(7):2116– 2123.
Chen, T., Embree, H. D., Brown, E. M., Taylor, M. M., Payne, G. F. 2003. Enzyme-catalyzed gel formation of gelatin and chitosan: potential for in situ applications. Biomaterials, 24(17):2831–2841.
Ebrahimi, R., Salavaty, M. 2018. Controlled drug delivery of ciprofloxacin from ultrasonic hydrogel. ePolymers, 18(2):187–195.
Florence, A. T., Attwood, D. 1998. Physicochemical Principles of Pharmacy, sixth edition. London. Macmillan Press. ISBN 9780857111746.
Hamidi, M., Azadi, A., Rafiei, P. 2008. Hydrogel nanoparticles in drug delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 60(15):1638–1649.
Hooper, D. C. 1999. Mode of Action of Fluoroquinolones. Drugs, 58(Supplement 2):6–10.
Hurst, M., Lamb, H. M., Scott, L. J., Figgitt, D. P. 2002. Levofloxacin: an updated review of its use in the treatment of bacterial infections. Drugs, 62(14):2127–2167.
Huynh, C. T., Nguyen, M. K., Lee, D. S. 2011. Biodegradable pH/temperature sensitive oligo (β- amino ester urethane) hydrogels for controlled release of doxorubicin. Acta Biomat, 7(8):3123– 3130.
Isık, B., Kıs, M. 2004. Preparation and determination of swelling behavior of poly (acrylamide-co- acrylic acid) hydrogels in water. Appl Polym Sci, 94(4):1526–1531.
Kadam, S., Dattatray, A., Landge, D. 2019. Formulation and evaluation of colon targeted matrix tablet of azathioprine. Indo American Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 9(7):3157–3168.
Kamboj, V. K., Verma, P. K. 2015. Poloxamers based nanocarriers for drug delivery system. Der Phar- macia Lettre, 7(2):264–269.
Katchalsky, A., Gillis, J. 1949. Theory of the potentiometric titration of polymeric acids. Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas, 68(9):879–897.
Kim, J. K., Basavaraja, C., Yamaguchi, T., Huh, D. S. 2013. Preparation and characterization of smart hydrogel nanocomposites sensitive to oxidation reduction. Polymer Bulletin, 70(1):207–220.
Moghimi, S. M., Hunter, A. C. 2000. Poloxamers and poloxamines in nanoparticle engineering and experimental medicine. Trends in Biotechnology, 18(10):412–420.
Mouzam, M. I., Dehghan, M. H. G., Asif, S., Sahuji, T., Chudiwal, P. 2011. Preparation of a novel floating ring capsule-type dosage form for stomach specific delivery. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal, 19(2):85–93.
Noel, G. J. 2009. A Review of Levofloxacin for the Treatment of Bacterial Infections. Clinical Medicine Insights, 1:433–458.
Pourjavadi, A., Mahdavinia, G. R. 2006. Super absorbency, pH-Sensitivity and Swelling Kinetics of Partially Hydrolyzed Chitosan-g-poly(Acrylamide) Hydrogels. Turkish Journal of Chemistry, 30(5):595–608.
Sagdinc, S., Bayari, S. 2004. Theoretical study of ofloxacin: geometrical parameters and vibrational wavenumbers. Journal of Molecular Structure: Theochem, 668(2-3):93–99.
Teo, B. M., Prescott, S. W., Ashokkumar, M., Grieser, F. 2008. Ultrasound initiated miniemulsion polymerization of methacrylate monomers. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 15(1):89–94.
Wan, T., Xiong, J., Zhao, Q. 2016. Crosslinker effects on swelling and gel properties of pH- and temperature responsive poly (NIPAM/IA/AM) hydrogels. Polym Bull, 73:1447–1458.
Wu, C., Wang, D., Wu, H., Dan, Y. 2016. Synthesis and characterization of macroporous sodium alginate-g-poly(AA-co-DMAPMA) hydrogel. Polym Bull, 73:3255–3269.
Wu, J., Lin, J., Li, G., Wei, C. 2001. Influence of the COOH and COONa groups and crosslink density of poly(acrylic acid)/montmorillonite superabsorbent composite on water absorbency. Polymer International, 50(9):1050–1053.
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.