Abstract
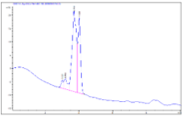
It is hard to overestimate the value of honey since the constituent substances in it are of great importance in the food industry and medicine. The quality of honey is established by the legislation of the Russian Federation (GOST). But the levels of these standards are regulated by outdated methods of analysis, which can not give reliable results. The detection of antibiotic residues in honey is a central issue in the quality and safety control of this product. Accumulation of drugs in honey used to treat bee colonies can cause allergies and dysbiosis in people who have eaten such honey, as well as develop antibiotic resistance in microorganisms. At present, one of the promising directions in the field of detecting medicines in honey is the use of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). It helps selectively and accurately detect antibiotic substances in honey bee productA sample preparation algorithm was developed, and the conditions for chromatographing combined indication of tetracyclines in honey at an acceptable concentration according to the MRL (0.01 mg/kg) with Agilent 1260 Infiniti liquid chromatograph equipped with a column thermostat, a gradient pump, and a UV detector were selected. Under these conditions, the antibiotic retention time was determined: 4.069 minutes for oxytetracycline, 4.331 minutes for tetracycline hydrochloride, 4.642 minutes for chlortetracycline. The developed HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of tetracycline antibiotics in honey was tested on honey bee products from the regions of the Republics of Tatarstan and Bashkortostan.
Full text article
Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.